Listen to the article
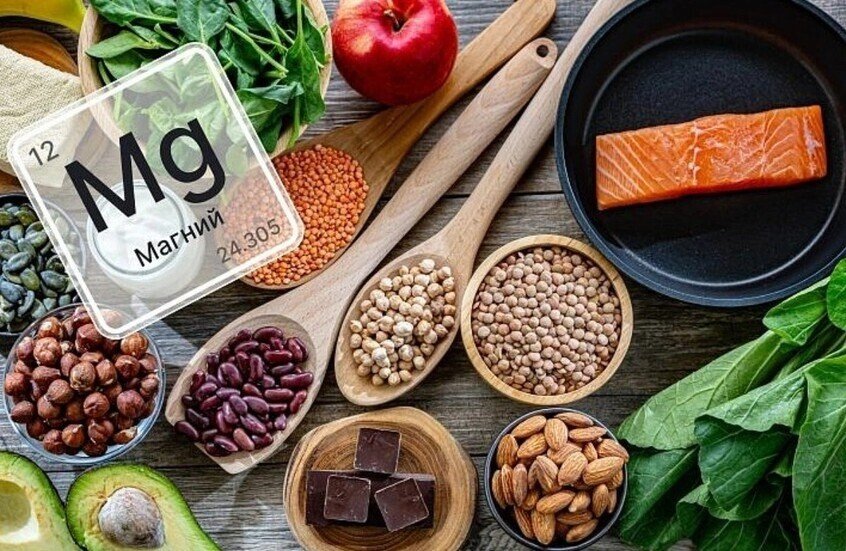
Magnesium deficiency remains a widespread issue despite the mineral’s presence in many foods, particularly during winter months and among individuals with poor nutrition or chronic diseases, according to Dr. Alexander Konkov. The essential mineral plays a critical role in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, making adequate magnesium intake vital for overall health and wellness.
Dr. Konkov explained that magnesium is fundamental for normal body functions, participating in muscle and nervous system operations, energy metabolism, cardiovascular function, and protein and DNA synthesis. The mineral’s involvement in such a wide range of biological processes underscores its importance for maintaining optimal health.
Who Needs Magnesium Supplementation
According to the expert, several groups face heightened magnesium requirements. Individuals experiencing chronic stress and high mental pressure benefit from the mineral’s ability to reduce nervous tension, improve sleep quality, and decrease anxiety levels.
Athletes and those engaged in strenuous physical labor require adequate magnesium levels because the mineral participates in muscle contraction and relaxation. Additionally, it reduces the risk of cramping while supporting energy metabolism and post-exercise recovery.
Patients with cardiovascular conditions and high blood pressure need sufficient magnesium to regulate heart function and maintain regular heartbeat. The mineral also helps control blood pressure levels, making it particularly important for this population.
Benefits for Women and Metabolic Health
Women during menstruation and menopause can experience relief from supplementation, as magnesium alleviates menstrual pain and helps stabilize hormonal balance. The mineral’s regulatory effects on body systems make it especially beneficial during these periods of hormonal fluctuation.
People suffering from metabolic disorders, diabetes, obesity, and kidney problems often experience low magnesium levels in their bodies. These conditions frequently correlate with magnesium deficiency, according to medical experts.
Health Benefits of Optimal Magnesium Levels
Dr. Konkov emphasized that maintaining optimal magnesium levels regularly contributes to mood regulation and reduces anxiety. The mineral prevents muscle cramps, maintains blood pressure and heart rate within normal ranges, and improves sleep quality.
Furthermore, magnesium participates in the absorption of calcium and vitamin D, which positively affects bone health. This interaction highlights the mineral’s role in skeletal system maintenance and overall structural integrity.
Safety Considerations and Dosage Guidelines
The expert noted that magnesium is relatively safe, especially when consumed with food. However, problems can arise from excessive magnesium supplement intake, including diarrhea, nausea, weakness, low blood pressure, and irregular heartbeat.
Individuals with chronic kidney disease should avoid magnesium supplements entirely, as the mineral may accumulate in the body and cause complications. Dr. Konkov stressed that the optimal dosage varies from person to person, depending on gender, age, physical activity, and health status.
The recommended average daily dose for adults ranges from 300 to 400 milligrams. Nevertheless, experts emphasize that magnesium supplements should not replace a balanced diet.
Natural Sources and Balanced Approach
Natural magnesium sources include nuts, seeds, legumes, whole grains, leafy vegetables, and dark chocolate. Combining a proper diet with supplements when necessary allows individuals to maintain optimal magnesium levels in the body.
Overall, magnesium is an extremely important mineral for the nervous system, muscles, heart, and bones. Its deficiency causes a wide range of symptoms, making proper supplementation crucial for affected individuals.
Medical professionals recommend that individuals consult with specialists to determine appropriate dosage and supplement form. Proper monitoring by healthcare providers helps maximize benefits while avoiding potential side effects associated with improper supplementation.